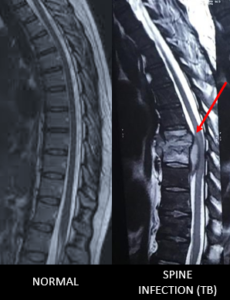
a) Vertebral Osteomyelitis:
Overview: Spinal infections is also called Vertebral Osteomyelitis. Infections in spine can be caused by various organisms like bacteria, fungi, etc. They usually spread from various parts of body through blood. Most common infection in India is Tuberculosis, which has been explained in detail below. Depending upon severity, infections may be treated medically or surgically.
b) Tuberculosis:
Overview: Tuberculosis is one of the most common infections in our country. It is estimated that almost 1/3rd to ½ of Indian population may have been infected with TB. However, there is a difference between infection and disease. Infection is present when the organism is harboured by an individual but does not cause symptoms. When a person’s immunity is affected due to varied reasons, this infection may become symptomatic and disease occurs. It is then when we need to treat it. TB can occur anywhere in the body. Lungs are the most common site, however, TB is most common spinal infection seen among patients in Indian subcontinent. TB is caused due to an organism called Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. This can spread to the spine through blood vessels from various parts of the body. Dorso-lumbar spine (back) is most commonly affected area. It can affect young and old alike. Patients usually complain of pain which develops over a few weeks not responding to usual treatment. There may be associated low grade fever, loss of weight and appetite. Depending upon neurological compression and level of lesion, patient may develop weakness (partial/complete) of arms/ legs. The destruction of bones and soft tissues by the organism may cause the spine to become unstable and development of Spinal Deformity. On clinical examination, there may be tenderness at the area of lesion. A thorough neurological examination is warranted. Past history of close contacts/ family members having TB hints diagnosis. The doctor may ask for X-rays (which are not very sensitive) and MRI. MRI usually shows soft tissues causing destruction and compression of neurological structures. However, many other diseases may have a similar radiological picture. For confirmation, a CT/ C-arm guided Biopsy is recommended. Based on reports and drug sensitivity, a course of Anti –Tuberculous Treatment (ATT) is advised in consultation of Chest Physician (TB Specialist). Since TB is an infection, medical management forms the core of treatment irrespective of surgery. ATT is a combination of 4-5 drugs given over a period of around 1 year depending upon response at serial intervals. Surgery is recommended only if the patient has severe pain not responding to ATT, neurological compression causing weakness or destruction of bones which may cause instability/ deformity. Based on the site of lesion, Cervical/ Dorsal/ Lumbar Anterior/Posterior Decompression and Stabilization is recommended.